-
Die Universität
- Herzlich willkommen
- Das sind wir
- Medien & PR
-
Studium
- Allgemein
- Studienangebot
- Campusleben
-
Forschung
- Profil
- Infrastruktur
- Kooperationen
- Services
-
Karriere
- Arbeitgeberin Med Uni Graz
- Potenziale
- Arbeitsumfeld
- Offene Stellen
-
Diagnostik
- Patient*innen
- Zuweiser*innen
- Gesundheitsthemen
- Gesundheitsinfrastruktur
Natalie Bordag
Intralesional and systemic immunometabolic characterization to advance combinatorial therapies in skin disease
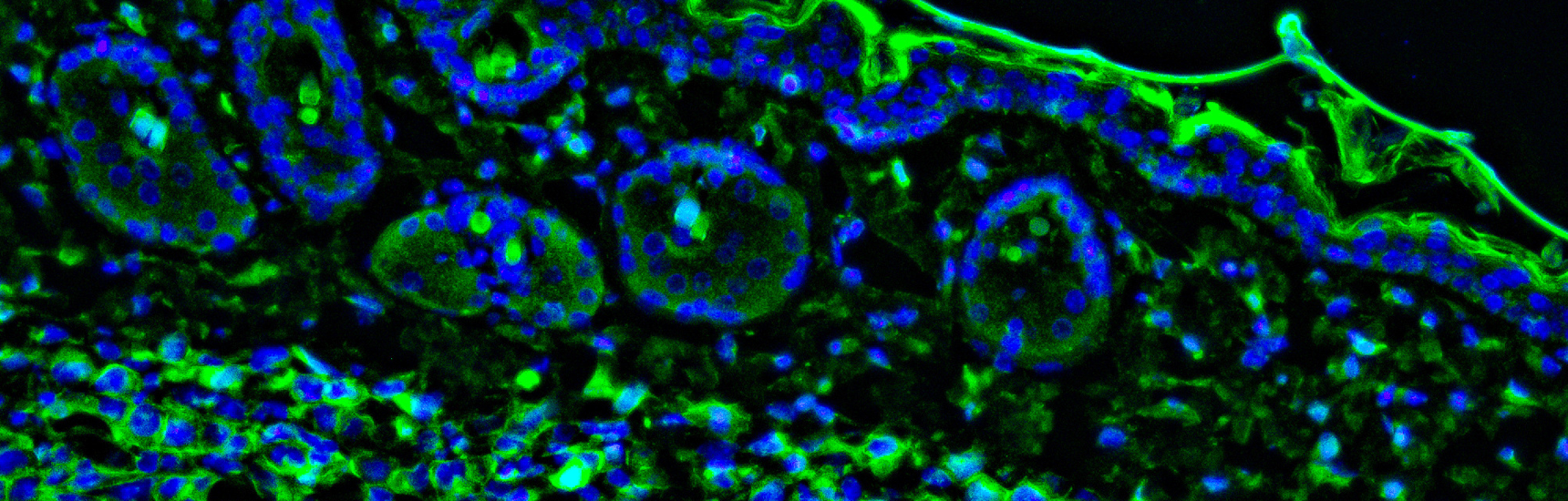
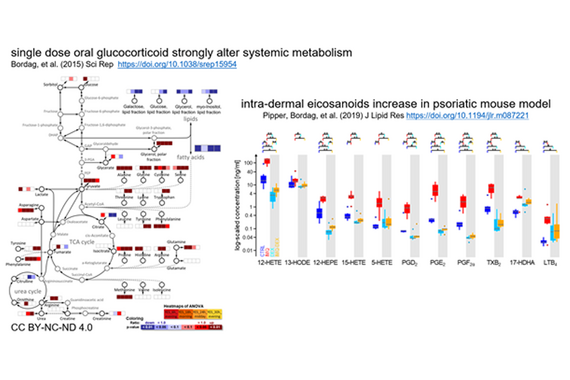
The dynamically growing field of immunometabolism cemented how crucial intracellular and systemic metabolism is in the regulation of immune cells. Psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, and other skin diseases driven by immune dysregulation are hypothesized to be treatable by targeting specific metabolic pathways. Therefore, the aim is to characterize intralesional and systemic interdependencies of metabolic and immunological changes in different skin disease to identify and test new therapeutic approaches. The focus is on repurposing existing metabolic medications with a high safety profiles suitable for long-term management and their synergistic combination with existing therapies to improve quality of life especially in chronic conditions.

Autobiography
Science is my passion. I studied Biochemistry in Leipzig, made my PhD in Biophysics Berlin. I dived into metabolomics at metanomics GmbH (a BASF company) and later at CBmed GmbH (K1-COMET center) in Graz building the metabolomics core-lab. At the LBI Lung Vascular Research and Department of Dermatology I deepen my immunological expertise in skin and pulmonary diseases. I enjoy working in teams with mutual respect, tolerance and integrity. I love to combine interdisciplinary approaches and to analyse results in depth with methods from classical statistics up to machine learning in order to excerpt useful results..